Kaiser Manzoor
Jamia Millia Islamia, India
Title: Biopolymers in Remediation of Wastewater: A Sustainable Approach Towards Environmental Engineering
Biography
Biography: Kaiser Manzoor
Abstract
Heavy metal poisoning in living systems has led to serious concerns disturbing ecosystems due to industrialization in developing as well as in developed countries. Huge amounts of toxic substances majority of which consists of heavy metal ions, dyes etc. is discharged into the water bodies on daily basis. The heavy metals include copper, cadmium, lead, arsenic and mercury, all of which are highly toxic to all forms of living systems. Besides EU Regulation1881/2006/ΕU have proposed that for aquatic life the permissible limits of Hg, Cd, Pb is 0.5 mg/kg, 0.05 mg/kg, 0.30 mg/kg, respectively. Arsenic mainly discharged from the pesticide industries causes drowsiness, brain damage, peripheral neuropathy and hemorrhages in humans. Cadmium is used in electroplating industries and it is categorized as human carcinogen by International Agency for Research on Cancer. Inhalation of the cadmium containing dust causes vomiting, respiratory tract and kidney problems, abdominal cramps and pulmonary edema. Copper is essential in low concentrations and is present in two forms bound to ceroplasmin and free form which is involved in reducing oxidative stress. However, its excess leads to impairment of zinc homeostasis which in turn causes disruption of antioxidant enzyme function thereby increasing oxidative stress.
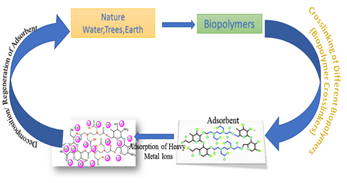 We have synthesized an adsorbent by simple esterification reaction by crosslinking carboxymethyl cellulose with chitosan using EDTA as crosslinker. Due to presence of the ample number of amine and hydroxyl groups the adsorption efficiency was increased sufficiently. A large number of evidences justify the strong chelation of the dipositive heavy metal ions by EDTA.Â
We have synthesized an adsorbent by simple esterification reaction by crosslinking carboxymethyl cellulose with chitosan using EDTA as crosslinker. Due to presence of the ample number of amine and hydroxyl groups the adsorption efficiency was increased sufficiently. A large number of evidences justify the strong chelation of the dipositive heavy metal ions by EDTA.Â
Â

